A thyroid biopsy is a diagnostic procedure used to evaluate thyroid nodules or masses. By obtaining a small tissue sample with a fine needle, specialists determine whether the nodule is benign or malignant.
The biopsy is performed under ultrasound guidance to ensure accuracy and minimize risk. It is usually quick, well-tolerated, and requires no special preparation. Local anesthesia may be used to reduce discomfort.
Complications are rare, but patients may experience mild pain, bleeding, or bruising at the puncture site. Serious risks are extremely uncommon when performed by experienced specialists.
Thyroid biopsy plays a crucial role in guiding treatment decisions. It helps distinguish between nodules that require surgery and those that can be safely monitored with regular follow-up.
What is a thyroid biopsy?
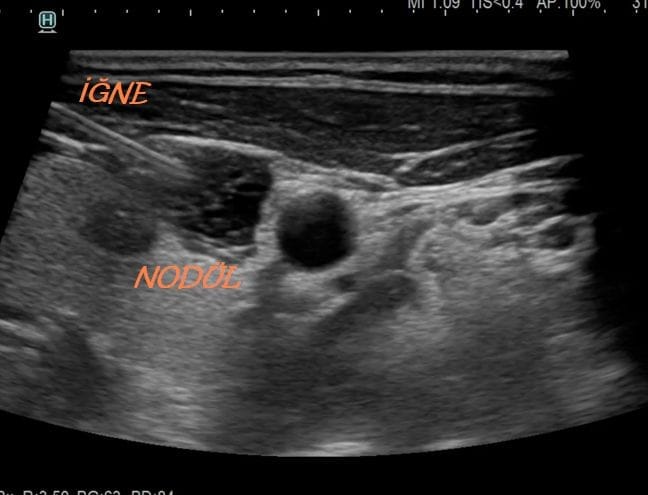
Thyroid biopsy is an important diagnostic method used to evaluate abnormalities in the thyroid gland. This procedure is especially necessary to determine whether nodules in the thyroid are benign or malignant. The thyroid gland is located at the front of the neck and plays important hormonal roles. Although nodules are usually harmless, in rare cases, they can turn into cancer. The biopsy procedure can be performed using different techniques:
- Fine needle aspiration biopsy,
- Core needle biopsy,
- Open biopsy,
When is a thyroid biopsy performed?
Thyroid biopsy is a procedure applied in certain cases to understand the nature of nodules in the thyroid gland. This method is especially preferred when a nodule or swelling is noticed in the thyroid gland. The presence of nodules is usually detected by the following methods:
- During physical examination,
- With ultrasound imaging,
- By radioactive thyroid scanning.
Biopsy may not be necessary for every nodule. However, for nodules of significant size or with suspicious appearance, a biopsy is recommended to determine whether they are benign or malignant.
Who should not undergo a thyroid biopsy?
There are certain cases where a thyroid biopsy is not performed, and these situations are clearly classified. First of all, if a thyroid nodule is larger than 4 cm, biopsy is not performed. Nodules of this size are usually treated with surgery or, in some cases, by biopsy followed by ablation, because biopsy may reduce diagnostic effectiveness in large nodules. In addition, biopsy is not performed for very high-risk nodules detected by ultrasound. Such cases require more advanced treatment and evaluation methods. Also, biopsy is not recommended for patients with thyroiditis, as inflammation can make biopsy results misleading. Finally, parathyroid adenomas can sometimes be confused with thyroid cancer:
- Thyroid nodule larger than 4 cm
- Patients with thyroiditis
- Suspicion of parathyroid adenoma
Which types of nodules are biopsied?
Thyroid nodules can be detected by palpation or ultrasonographic methods. Especially ultrasonographic examination allows detailed evaluation of nodules. Determining nodules with suspicion of cancer can be done more objectively with this method. The referral of suspicious nodules for biopsy depends on various features:
- Nodules exceeding a certain size threshold,
- Nodules with irregular borders,
- Nodules containing calcifications,
- Nodules with hypoechoic structure.
How is a thyroid biopsy performed?
Fine needle biopsy is preferred to examine the content of thyroid nodules. The patient’s skin is first cleaned with an antiseptic solution and local anesthesia may be applied. The doctor inserts a very fine needle into the thyroid nodule under ultrasound guidance. Cell samples are drawn from the nodule with the needle, and if necessary, the procedure can be repeated to obtain multiple samples. The average duration is about half an hour, and it is generally performed without the need for surgery.
What are the advantages of thyroid biopsy?
This procedure offers the opportunity to analyze the contents of nodules that cannot be determined by ultrasound more clearly. Pathological examination is very effective in determining whether the nodules are malignant. Thanks to this verification, unnecessary surgeries for patients with suspected cancer are prevented. Also, if the nodule is malignant, biopsy results determine how extensive the surgery should be. The advantages of thyroid biopsy include:
- Fast results: Biopsy techniques speed up the diagnostic process.
- Economic cost: Most biopsy methods are less costly compared to other surgical interventions.
- Comfortable procedure: Patients usually experience low pain and a short procedure.
- Reliability: Biopsy provides high reliability in understanding the nature of thyroid nodules.
What is the process after a thyroid biopsy?
The process after a thyroid biopsy varies depending on the method used. Immediately after fine needle biopsy, pressure is applied to the biopsy area for 20 minutes. This helps prevent bleeding. After the pressure, no bandage is needed. However, it is recommended to be careful to protect the area from infection on the first day.
Is a thyroid biopsy painful?
The pain felt during a thyroid biopsy varies depending on the technique used. Fine needle aspiration biopsy is generally considered painless because it is performed under local anesthesia. During this process, the patient keeps their head tilted back in a fixed position, which may cause slight discomfort, but this feeling is usually temporary and does not cause serious pain.
Is fine needle aspiration biopsy of the thyroid risky?
Fine needle aspiration biopsy of the thyroid is a method frequently preferred in the evaluation of thyroid nodules. This procedure is generally considered safe, but it may rarely carry some risks. These risks are usually mild and manageable. Performing the procedure under ultrasound guidance reduces the risk of complications. However, some situations should be considered:
- Bleeding may occur in the biopsy area.
- There is a possibility of infection.
- Structures close to the thyroid gland may be damaged.
Although such complications are very rare, the existing risks should be known by patients and healthcare professionals. Also, the result of the biopsy may not always be definitive, so a repeat biopsy may rarely be required.
Thyroid Biopsy Reviews
For comments from Prof. Dr. Özgür Kılıçkesmez, you can check Google Maps or Doktortakvimi.
Frequently Asked Questions

Is a thyroid biopsy painful?
The patient generally does not feel pain during a thyroid biopsy. Since needle aspiration biopsy is performed with local anesthesia, there is no pain during the procedure. However, the patient must keep their head still, which may cause slight discomfort.
Are the results of a thyroid biopsy available immediately?
Thyroid biopsy results are not available immediately. Usually, the results are ready within a few days after the procedure is completed. This period may vary depending on the workload of the laboratory. Also, the time needed to examine the tissue sample may be extended according to the complexity of the sample. Therefore, patients are advised to be patient while waiting for results. This waiting period should be spent without unnecessary worry.
How many minutes does a thyroid biopsy take?
Including the preparation phase, a thyroid biopsy is usually completed within 5 to 10 minutes. This time frame should be considered when planning the procedure. The duration may vary depending on the number of nodules to be biopsied and the doctor’s technique. In general, patients should know that the procedure will be completed within this period.
What should be considered after a thyroid biopsy?
Patients should take some precautions after a thyroid biopsy. First, the biopsy area should be kept clean and dry. Strenuous physical activity should be avoided for the first few days. In addition, pressure should not be applied to the biopsy area and heavy lifting should be avoided. If the patient notices excessive redness, swelling, or bleeding at the biopsy site, they should contact their doctor. If pain is felt in the first days after the procedure, painkillers recommended by the doctor can be used. During this period, the patient should strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations.
Is general anesthesia used during a thyroid biopsy?
General anesthesia is usually not necessary during a thyroid biopsy. Only the area to be biopsied is numbed with local anesthesia during fine needle biopsy, so the patient does not feel pain and remains conscious during the procedure. However, if an open biopsy is to be performed, the situation may be different.
Can I take a shower after a thyroid biopsy?
Patients are often concerned after a thyroid biopsy, but it should be known that it is a very simple procedure. After the biopsy, it is recommended to wait one day and protect the biopsy area during this period. The next day, the protective band on the biopsy area can be carefully removed. Once the band is removed, the patient can allow the area to come into contact with water and start bathing slowly. During this process, it is recommended to clean the biopsy area gently. If there is excessive sensitivity or pain in the area, it is best to contact the doctor.
Additional Resources and Documents

Girişimsel Radyoloji ve Nöroradyoloji Uzmanı Prof. Dr. Özgür Kılıçkesmez, 1997 yılında Cerrahpaşa Tıp Fakültesi’nden mezun oldu. Uzmanlık eğitimini İstanbul Eğitim ve Araştırma Hastanesi’nde tamamladı. Londra’da girişimsel radyoloji ve onkoloji alanında eğitim aldı. İstanbul Çam ve Sakura Şehir Hastanesi’nde girişimsel radyoloji bölümünü kurdu ve 2020 yılında profesör oldu. Çok sayıda uluslararası ödül ve sertifikaya sahip olan Kılıçkesmez’in 150’den fazla bilimsel yayını bulunmakta ve 1500’den fazla atıf almıştır. Halen Medicana Ataköy Hastanesi’nde görev yapmaktadır.




Vaka Örnekleri