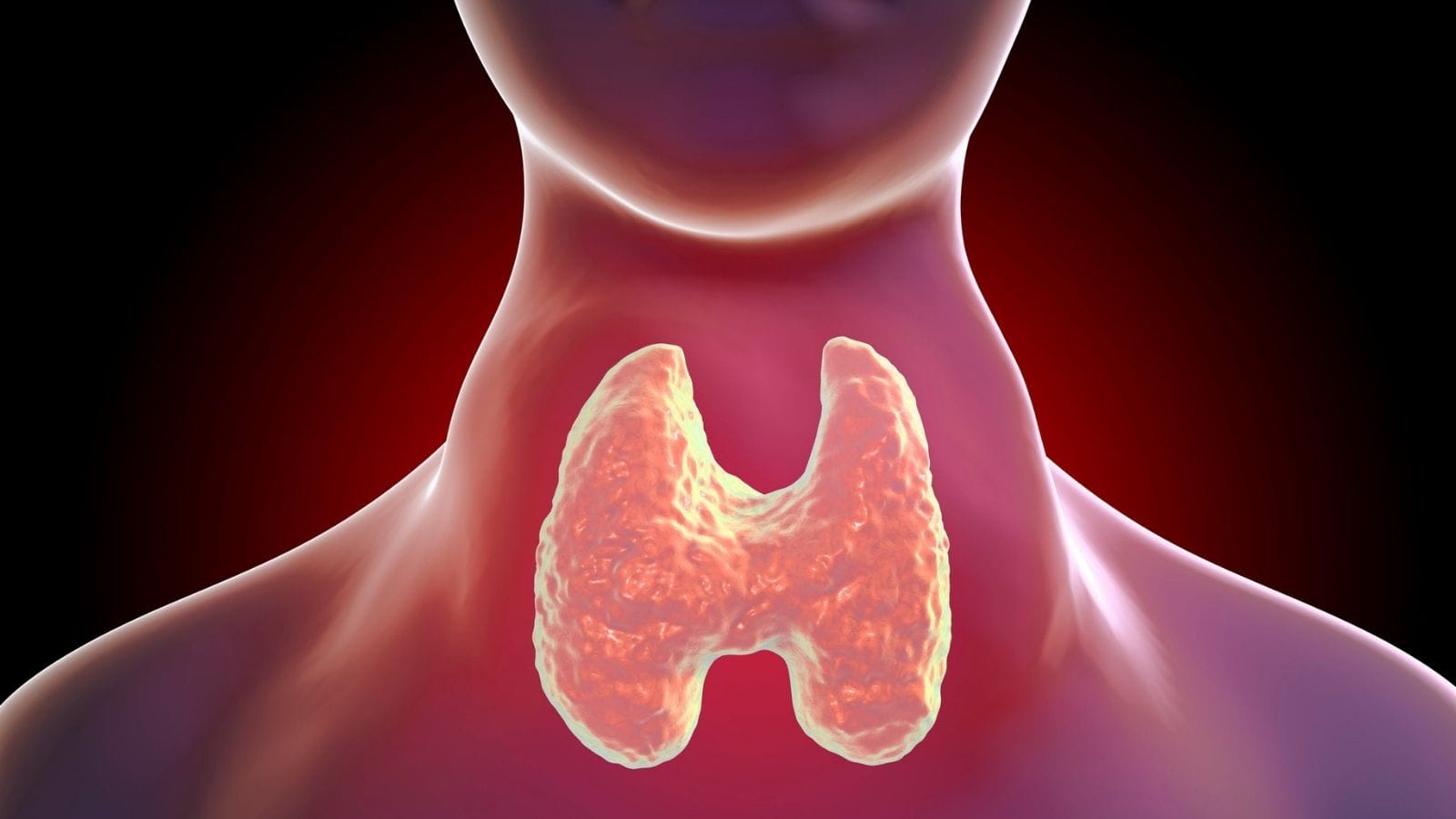
Hoarseness and difficulty swallowing may signal underlying thyroid disease. Enlarged thyroid tissue, nodules, or tumors can press on the larynx and esophagus, leading to vocal changes and swallowing problems.
Goiter is a common cause of such symptoms. Enlargement of the gland compresses nearby structures, creating persistent throat discomfort. Evaluation with ultrasound and blood tests is recommended in these cases.
Thyroid cancer can also cause hoarseness and dysphagia by invading surrounding tissues. Early detection through biopsy and imaging ensures timely treatment and prevents disease progression.
Patients experiencing persistent hoarseness or swallowing difficulties should seek endocrinological assessment. Prompt diagnosis allows targeted treatment, improving both symptom relief and long-term health outcomes.
Prof. Dr. Özgür KILIÇKESMEZ Prof. Dr. Kılıçkesmez holds the Turkish Radiology Competency Certificate, the Turkish Interventional Radiology Competency Certificate, Stroke Treatment Certification, and the European Board of Interventional Radiology (EBIR). In his academic career, he won the Siemens Radiology First Prize in 2008.
Interventional Radiology / Interventional Neuroradiology
What Is the Connection Between Hoarseness and Thyroid Disorders?
Because the thyroid gland is located close to the vocal cords and laryngeal nerve, thyroid disorders can cause hoarseness. Due to this relationship, both benign and malignant thyroid nodules, when enlarged, may compress the nerve and affect vocal cord function. When the nerve is compressed, vocal cord impairment occurs, presenting as hoarseness or voice changes. This is commonly seen when an enlarged thyroid gland presses on surrounding tissues in conditions such as goiter, thyroiditis, and thyroid cancer.
Especially common causes include:
- Thyroid Nodules: Create changes in voice quality by exerting physical pressure on the nerve.
- Thyroid Inflammation (Thyroiditis): Causes swelling that presses on the larynx and vocal cords.
- Hypothyroidism: Leads to fluid accumulation in the vocal cords, causing thickening.
Can Thyroid Problems Cause Difficulty Swallowing?
Thyroid problems may arise due to enlargement of the thyroid gland or formation of nodules in the neck, which can cause difficulty swallowing. Because the thyroid gland is located very close to the esophagus and trachea, an enlarged thyroid can put pressure on these structures. Especially goiter formation and nodules can cause a sensation of “a lump in the throat,” known as the globus sensation, during swallowing.
In more advanced cases, this pressure may negatively affect swallowing function, and in some situations, breathing difficulties may occur. For this reason, growing nodules or goiter can compress the esophagus and make it difficult to swallow solid foods. Especially during physical activity or while lying down, breathing may become harder as the enlarged thyroid can press on the trachea.
In addition, several different factors can cause thyroid enlargement:
- Goiter: In this case, the thyroid gland may enlarge, affecting the normal production of thyroid hormones.
- Nodules: Large nodules may become big enough to compress surrounding tissues.
- Thyroid diseases: Disorders such as Graves’ disease or Hashimoto’s thyroiditis can also cause thyroid enlargement.
These conditions may result in dysphagia, a sensation of a lump in the throat, and in some cases, difficulty breathing. Early medical evaluation is recommended for individuals experiencing these symptoms.
*We recommend filling out all fields so we can respond in the best possible way.
What Are the Specific Thyroid Conditions Associated With These Symptoms?
Certain thyroid conditions may compress surrounding tissues, leading to symptoms such as hoarseness and difficulty swallowing. These include thyroid nodules, goiter, and thyroid cancer. Each of these can cause such symptoms due to their unique features.
- Thyroid Nodules: Nodules are abnormal growths or masses in the thyroid gland that, in some cases, may press on surrounding tissues. Large nodules, in particular, can compress the voice box or esophagus, leading to hoarseness, difficulty swallowing, and sometimes breathing problems. Most nodules are benign, but some may be malignant. Hyperactive nodules can cause hormonal imbalances, resulting in additional symptoms.
- Goiter: Characterized by enlargement of the thyroid gland, goiter may occur due to iodine deficiency or autoimmune diseases. Large goiters may press on surrounding tissues, causing a feeling of fullness in the throat, difficulty swallowing, and hoarseness. Some goiters are visible from the outside and can make breathing more difficult, especially while lying down.
- Thyroid Cancer: Like nodules, thyroid cancer can grow and compress surrounding tissues, leading to voice changes and difficulty swallowing. Aggressive types can rapidly spread to surrounding tissues, increasing the severity of symptoms.
When Should Medical Attention Be Sought for These Symptoms?
If symptoms such as hoarseness and difficulty swallowing persist for more than three to four weeks, medical attention is recommended. These symptoms may indicate serious conditions such as goiter or thyroid nodules. Therefore, if symptoms last longer, expert evaluation is important to understand the seriousness of the situation.
As a result of thyroid gland enlargement or the development of nodules, the following may occur:
- Pressure on the vocal cords and esophagus may affect their normal functions
- May cause difficulty swallowing, known as dysphagia
- May cause narrowing of the airways, making it difficult to breathe
If these symptoms become persistent, thyroid enlargement and related complications may occur. Early diagnosis is crucial for preventing the progression of such disorders and worsening symptoms. In addition, delayed treatment may result in serious health problems such as thyroid cancer. Therefore, if these symptoms persist, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional promptly.
In conclusion, persistent hoarseness or difficulty swallowing may indicate underlying thyroid dysfunction, making early evaluation a critical step. Especially when these symptoms are due to goiter or nodules, they may lead to serious complications if not treated properly. Therefore, when the duration of symptoms is prolonged, seeking medical attention without delay is vital for health.
What Treatment Options Are Available for Hoarseness and Difficulty Swallowing Related to the Thyroid?
Various interventional radiology approaches are preferred in the treatment of thyroid-related hoarseness and difficulty swallowing. These treatment options are especially useful for patients seeking alternatives to surgery or those who wish to alleviate complications after surgery. Each method offers different advantages in reducing pressure on the vocal cords and esophagus.
- Percutaneous Ethanol Injection (PEI): This minimally invasive method involves injecting ethanol into thyroid nodules to shrink them. In this way, the pressure nodules exert on the vocal cords is reduced, easing complaints such as difficulty swallowing.
- Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA): The RFA method uses thermal energy to shrink thyroid nodules. As it does not require surgery, it is considered a good option for patients wishing to avoid surgery.
- Fine-Needle Aspiration (FNA) and Biopsy: Performed under ultrasound guidance, this procedure is used to determine whether thyroid nodules are malignant. If malignancy is suspected, more advanced treatment methods may be necessary.
- Ultrasound-Guided Treatments: Treatments such as microwave ablation or laser ablation target small thyroid nodules, thereby reducing pressure on surrounding structures.
- Vocal Cord Medialization: Helps resolve complaints such as hoarseness that develop after surgery. This option aims to reduce postoperative complications.

Girişimsel Radyoloji ve Nöroradyoloji Uzmanı Prof. Dr. Özgür Kılıçkesmez, 1997 yılında Cerrahpaşa Tıp Fakültesi’nden mezun oldu. Uzmanlık eğitimini İstanbul Eğitim ve Araştırma Hastanesi’nde tamamladı. Londra’da girişimsel radyoloji ve onkoloji alanında eğitim aldı. İstanbul Çam ve Sakura Şehir Hastanesi’nde girişimsel radyoloji bölümünü kurdu ve 2020 yılında profesör oldu. Çok sayıda uluslararası ödül ve sertifikaya sahip olan Kılıçkesmez’in 150’den fazla bilimsel yayını bulunmakta ve 1500’den fazla atıf almıştır. Halen Medicana Ataköy Hastanesi’nde görev yapmaktadır.







Vaka Örnekleri