Venous insufficiency is a condition where leg veins fail to efficiently return blood to the heart. It causes swelling, varicose veins, and skin changes. Early treatment helps reduce complications and improve circulation in affected patients.
Common symptoms of venous insufficiency include heaviness, cramps, and pain in the legs. Over time, skin discoloration, itching, and ulcers may develop, particularly around the ankles, requiring medical evaluation.
Conservative management involves compression stockings, exercise, and leg elevation. These methods support venous return, relieve symptoms, and slow disease progression, especially in mild to moderate cases.
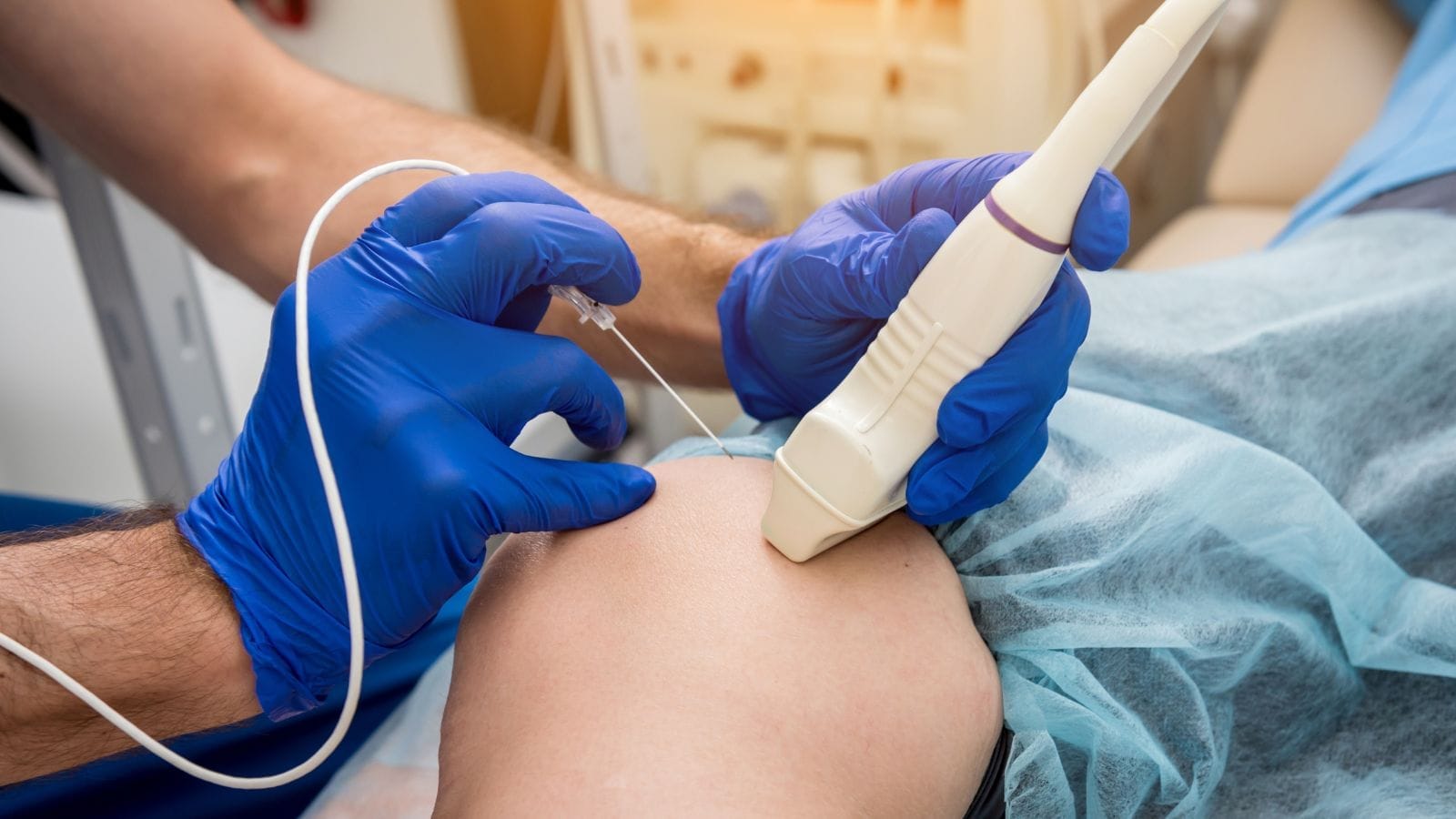
Advanced treatments include endovenous ablation, sclerotherapy, and minimally invasive embolization. These interventional radiology techniques close faulty veins, redirect blood flow, and provide long-term relief with low complication rates.
What Are the Symptoms of Venous Insufficiency?
The symptoms of venous insufficiency may vary from person to person, but there are certain common points. The most prominent sign is swelling in the legs, which becomes more noticeable after prolonged sitting or standing. Additionally, pain, throbbing, or a feeling of heaviness in the legs are among the frequently observed symptoms. These pains usually decrease when the legs are elevated.
Visible signs of venous insufficiency include varicose veins:
- Enlarged, twisted veins in the legs that are easily noticeable under the skin.
Skin changes are also important signs of venous insufficiency:
- Dark brown patches around the ankles,
- Eczema-like skin disorders,
- Hardening and thickening of the skin (lipodermatosclerosis).
Other symptoms include frequent nighttime cramps or muscle spasms in the legs, and itchy or sometimes reddened skin. The most serious sign is leg ulcers around the ankles that are difficult to heal. Restless leg syndrome, which presents as an uncontrollable urge to move the legs, is another condition caused by venous insufficiency.
What Causes Venous Insufficiency?
Venous insufficiency is caused by the inability of the leg veins to return blood to the heart adequately. This health issue is associated with various factors:
Deep Vein Thrombosis:
Clots in the leg veins disrupt blood flow and can damage the valves.
Sedentary lifestyle:
Prolonged sitting or standing increases pressure in the veins.
Lack of physical activity:
Low levels of exercise weaken the blood-pumping function.
Obesity:
Excess weight puts additional strain on the veins.
Pregnancy:
Hormonal changes and increased blood volume affect vein function.
Smoking:
Damages the circulatory system and impairs vein health.
High blood pressure:
Constant high pressure in the leg veins can impair valve function.
Phlebitis:
Inflammation of the veins prevents proper valve function.
Genetic factors and age:
Family history and aging increase the risk.
Pelvic tumors:
Rarely, these tumors may block veins and cause problems.
These factors weaken the venous valves and cause blood to pool in the legs. With effective management and early intervention, venous insufficiency can be controlled.
How Is Venous Insufficiency Diagnosed?
The diagnosis of venous insufficiency requires a detailed process. It begins with a review of the patient’s medical history. The healthcare professional thoroughly evaluates symptoms such as swelling, skin changes, and varicose veins in the legs. Physical examination is a cornerstone of diagnosis and plays a critical role in making an accurate assessment. Advanced imaging techniques are used to confirm the diagnosis:
Duplex Ultrasound:
This method is primarily used to evaluate blood flow and the condition of the veins. By combining conventional ultrasound and Doppler technology, it analyzes the speed and direction of blood flow.
Doppler Ultrasonography:
Especially used for examining large veins in the legs, providing detailed information about blood flow.
Magnetic Resonance Venography (MRV):
Required for the detection of deep vein thrombosis. It provides highly detailed images of the veins but has limitations such as metal implants.
Computed Tomography Venography (CTV):
Used when more detailed visualization of venous structures is needed. It is less commonly preferred due to the use of radiation and contrast material.
Phlebography:
This method involves injecting a contrast dye into the veins and imaging with X-ray. It is mostly used when other methods are insufficient or when surgery is being planned.
What Are the Treatment Methods for Venous Insufficiency?
Treatment options for venous insufficiency aim to relieve symptoms and improve blood flow. Thanks to minimally invasive methods, patients can return to normal life in a short time. Treatment methods include:
- Endovenous Laser Ablation (EVLA) and Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) close veins with heat. These methods, applied under local anesthesia, offer rapid recovery.
- Sclerotherapy is especially suitable for small veins. It involves collapsing the veins using a chemical foam.
- Non-Thermal Ablation techniques close veins without heat, minimizing the risk of nerve damage.
- Microphlebectomy involves removing superficial veins near the skin. It is usually performed under local anesthesia.
- Vein Stripping and Ligation is the removal of larger veins. It is less commonly preferred today.
- Debridement involves cleaning dead tissue to accelerate the healing of venous ulcers.
How Can Venous Insufficiency Be Prevented?
Preventing venous insufficiency is possible through healthy lifestyle choices. First, regular physical activity is important; exercises such as walking, swimming, and cycling increase blood circulation and strengthen leg muscles. Elevating the legs above heart level also improves blood flow. Wearing compression stockings, especially, helps the veins in the legs work more effectively.
Maintaining an ideal weight reduces pressure on the veins and supports blood circulation. Avoiding long periods in the same position—moving regularly while sitting or standing—prevents blood from pooling in the legs. Avoiding smoking is a critical step for vein health. Adopting a heart-friendly diet also benefits overall health.
Consuming adequate water and maintaining regular skin care help prevent venous insufficiency. Protecting skin health reduces the risk of irritation and infection associated with venous insufficiency. Some supplements, such as horse chestnut extract, may help relieve symptoms; however, always consult a healthcare professional before starting any supplement.
What Are the Complications of Venous Insufficiency?
Complications of venous insufficiency highlight the seriousness of this condition and the need for intervention. Chronic venous insufficiency can lead to various health problems in the body. Firstly, venous ulcers appear as painful wounds on the lower legs. These do not heal over time and increase the risk of infection. Secondly, deep vein thrombosis, which is the formation of blood clots in deep veins, can occur. These clots can break off, travel to the lungs, and cause pulmonary embolism.
Venous Ulcers:
Painful, slow-healing wounds that form on the lower legs.
Blood Clots:
Increase the risk of deep vein thrombosis in the legs.
Bleeding:
Severe bleeding may occur from venous ulcers or ruptured varicose veins.
Skin Changes:
Brown discoloration, eczema, and lipodermatosclerosis may be seen.
Secondary Lymphedema:
Damage to the lymphatic system causing tissue swelling.
Infections:
Increased risk of infection due to skin breakdown and ulcers.
Pain and Discomfort:
Persistent pain, heaviness, itching, and cramps in the legs.

Interventional Radiology and Neuroradiology Speaclist Prof. Dr. Özgür Kılıçkesmez graduated from Cerrahpaşa Medical Faculty in 1997. He completed his specialization at Istanbul Education and Research Hospital. He received training in interventional radiology and oncology in London. He founded the interventional radiology department at Istanbul Çam and Sakura City Hospital and became a professor in 2020. He holds many international awards and certificates, has over 150 scientific publications, and has been cited more than 1500 times. He is currently working at Medicana Ataköy Hospital.






Vaka Örnekleri