A kidney biopsy is a diagnostic procedure used to examine kidney tissue under a microscope. It helps identify the cause of kidney disease, evaluate severity, and determine the most effective treatment plan.
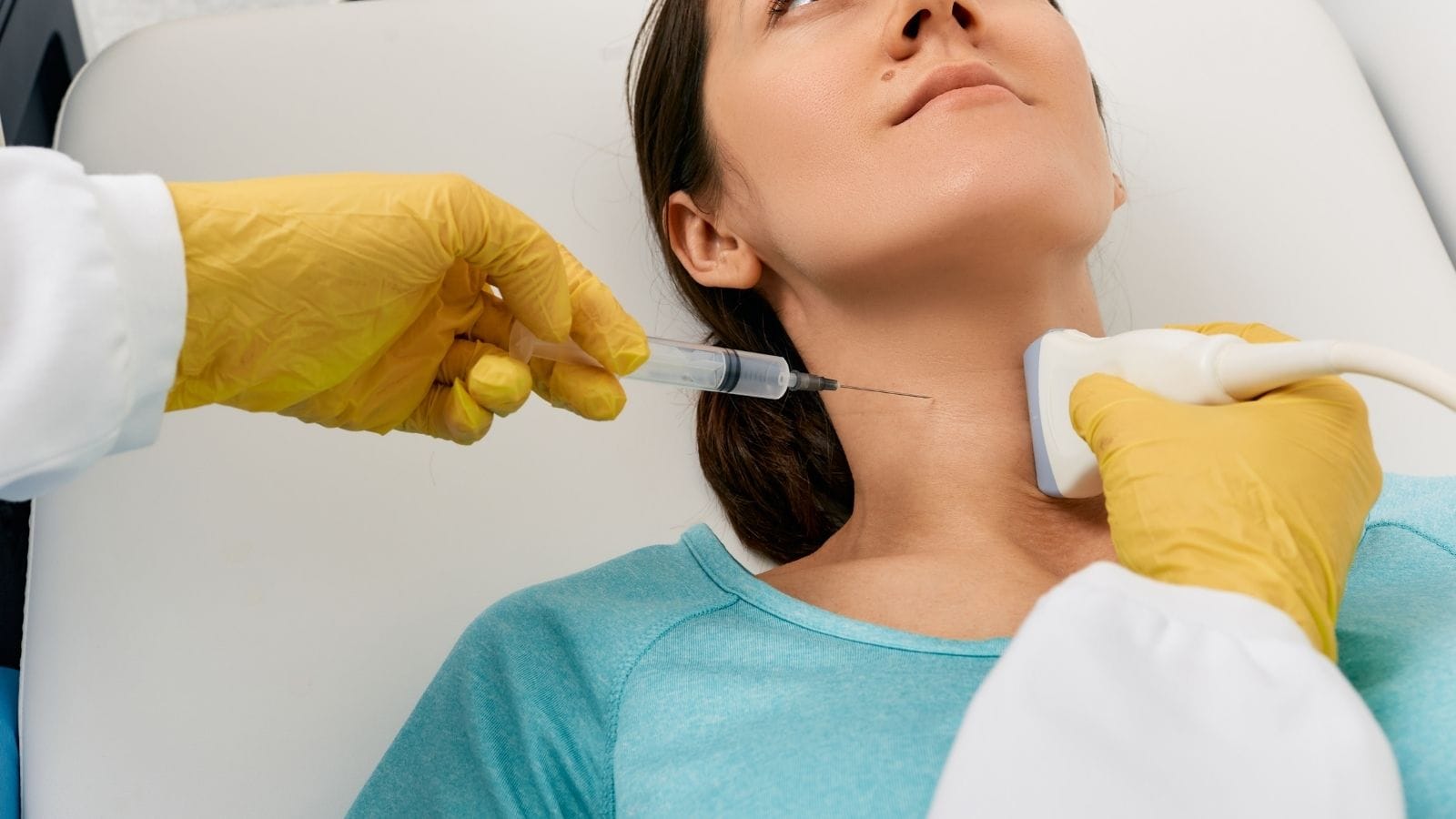
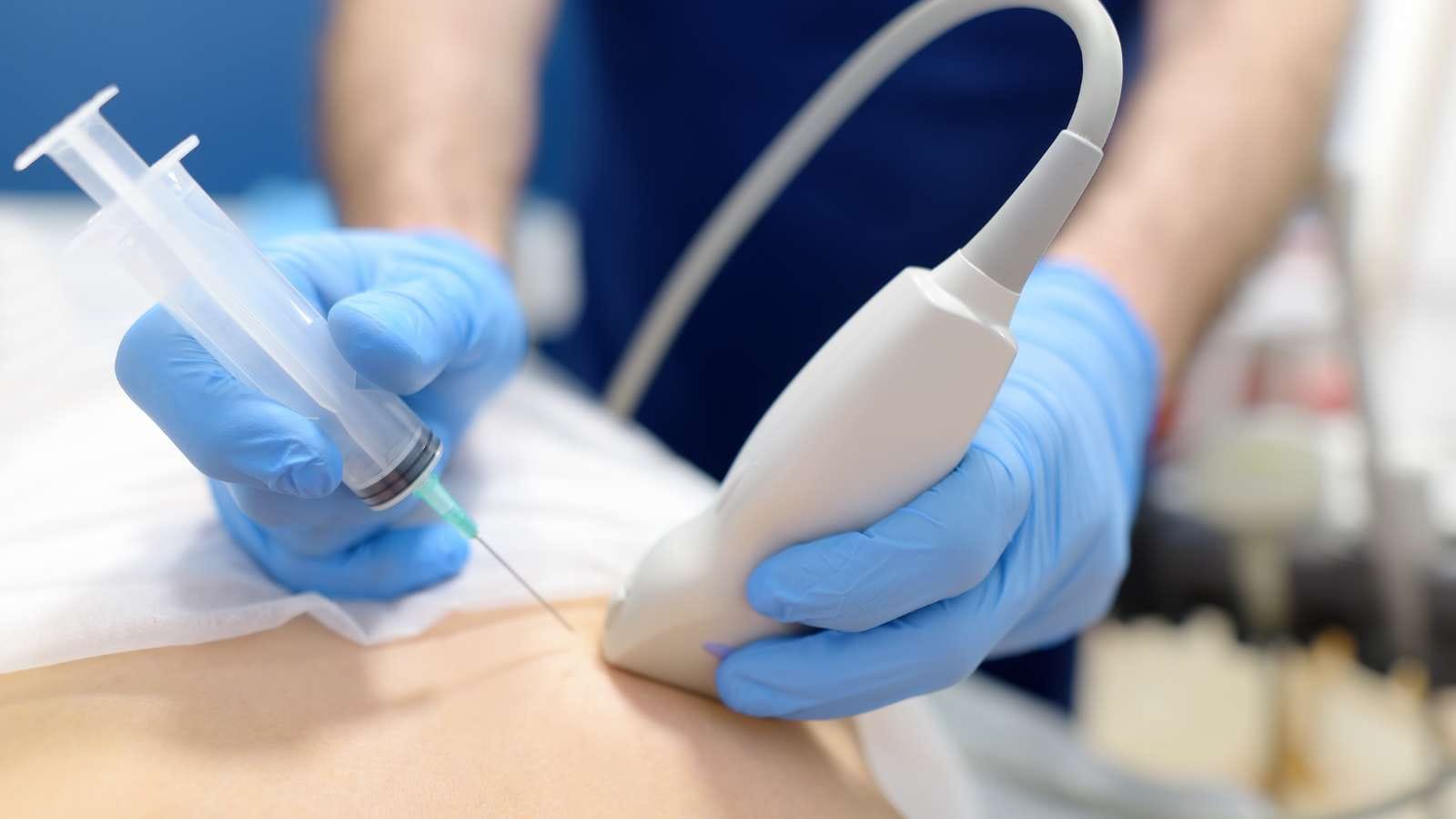
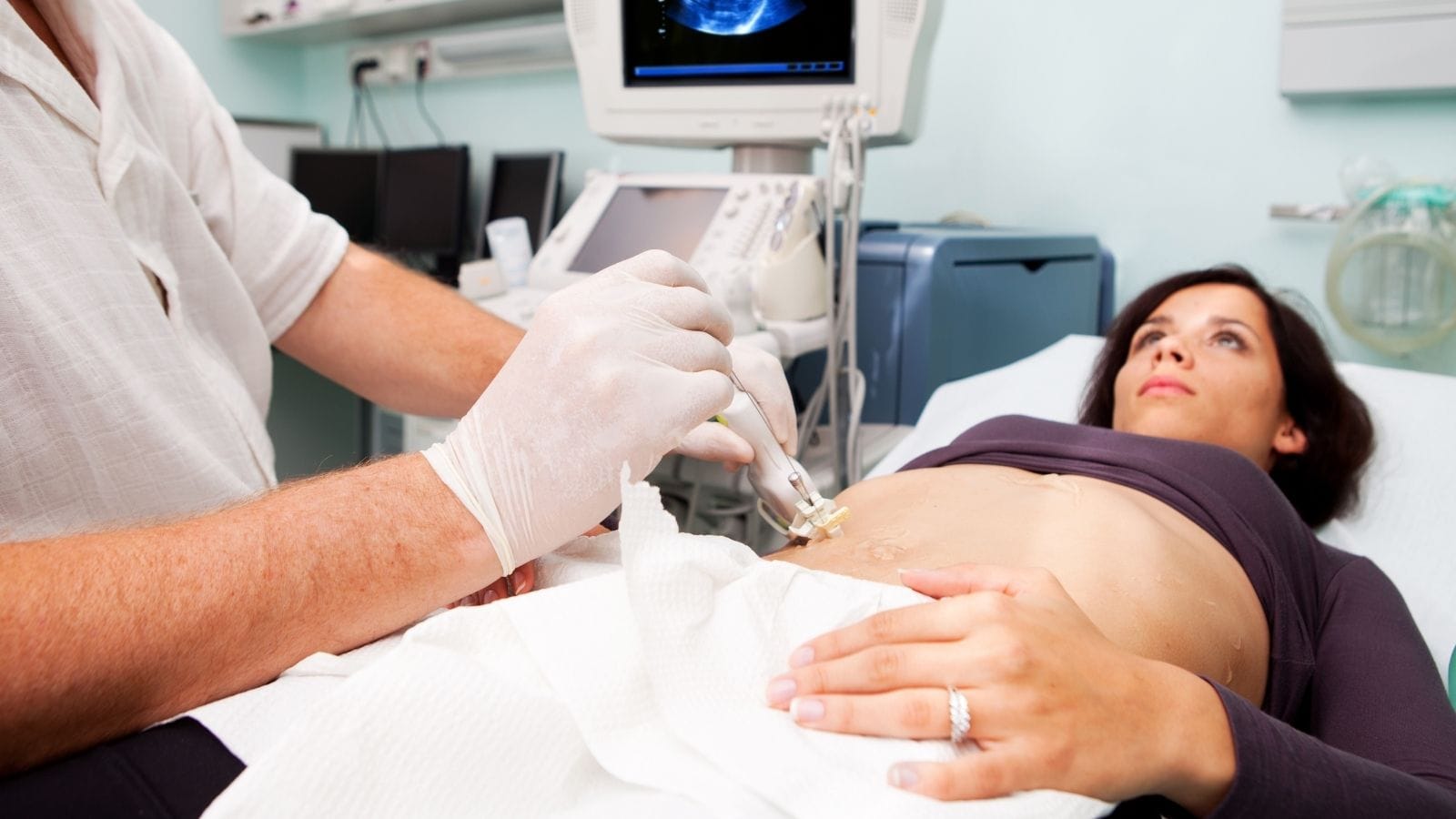
The procedure is usually performed under ultrasound or CT guidance. A thin needle is inserted into the kidney to collect a small tissue sample, minimizing the risk of complications.
Mild pain or bleeding at the biopsy site may occur, but serious complications are uncommon. Patients are monitored closely after the procedure to ensure safety before discharge.
Kidney biopsy provides essential information for managing conditions such as glomerulonephritis, nephrotic syndrome, and unexplained renal dysfunction, guiding personalized and effective treatments.
What Is a Kidney Biopsy?
Kidney biopsy is a method used for definitive diagnosis of diseases. In particular, other tests may be insufficient for diagnosing certain kidney diseases. In these cases, doctors perform a kidney biopsy for an accurate diagnosis. A thin needle is used to obtain a sample from the kidney tissue. During this procedure, ultrasound or tomography is used to guide the doctor to perform the process safely and correctly. The position of the needle and kidney is continuously monitored on a screen during the procedure.
Tissue samples taken during kidney biopsy are sent to the laboratory to determine the type and severity of the disease. The collected tissue plays a major role in identifying various diseases. This method is especially important for the following situations:
- Detecting tissue rejection,
- Diagnosing kidney diseases such as glomerulonephritis,
- Investigating unexplained kidney failure.
What Is the Purpose of a Kidney Biopsy?
Kidney biopsy is performed for two main purposes. First, it is used to accurately diagnose kidney diseases that cannot be identified despite detailed examinations. The tissue samples obtained during this process provide critical information to understand the type and course of the disease. The second purpose is to determine the nature of tumors detected in the kidney. With kidney biopsy, it is confirmed whether the tumor is benign or malignant. This information forms the basis for the following steps:
- Determining whether the tumor is benign or malignant.
- Planning treatment based on the type of disease.
- Performing tumor-specific classifications.
Not every kidney tumor is evaluated with biopsy. In particular, direct surgical intervention may be preferred in tumors that are large or show obvious signs.
How Is a Kidney Biopsy Performed?
Care is taken to ensure patient comfort and procedure success during a kidney biopsy. The procedure begins with the patient lying face down on a bed, using an ultrasound device. A pillow is placed under the patient’s lower abdomen to raise the lumbar region, providing an optimal position for the procedure. The lumbar and back regions are left exposed, and sterilization is completed. The area where the procedure will be performed is clearly visualized using ultrasound. Important points for determining the ideal needle entry site include:
- Preferring peripheral areas of the kidney with less blood flow.
- After sterilization, the entry site and its surroundings are made sterile again.
Anesthesia is started with a thin needle. After numbing the area, a 1–2 mm incision is made, and tissue sampling is performed with a tru-cut needle. The progress of the needle is monitored with ultrasound. When the needle reaches the targeted tissue area, the patient is asked to hold their breath briefly. During this stage, color Doppler ultrasound is used to detect possible bleeding. After the tissue is sampled, the biopsy procedure is completed, and the entry site is bandaged and sterilized.
What Should Be Considered Before Kidney Biopsy?
The precautions to be taken before a kidney biopsy are very important for the patient’s health. First, the doctor reviews the patient’s current blood tests. If there is a risk of bleeding, this is assessed in more detail. If the patient’s previous tests are up to date, new testing may not be necessary. Blood-thinning medications should be discontinued one week before the procedure. The status of the kidney tissue is evaluated based on ultrasound and tomography results, and an appropriate treatment plan is created. The patient should fast for at least 7 hours before the biopsy. If the patient is on chronic medication, it can be taken with a small amount of water.
What Is the Post-Kidney Biopsy Process?
There are some important points patients should pay attention to after a kidney biopsy. During the first 24 hours after the procedure, it is recommended that the patient refrain from excessive movement. Avoiding heavy physical activities is highly important during this period. Usually, patients who undergo biopsy should rest during the first few hours after the procedure.
- The patient should rest in bed for at least 4 hours.
- Unless otherwise stated by the doctor, patients may resume eating after the procedure.
- Drinking plenty of fluids is recommended.
Mild bleeding that may occur after the biopsy usually resolves on its own within a few days. This may be observed as a temporary change in urine color.
When Is a Kidney Biopsy Recommended?
Kidney biopsy is a procedure recommended by doctors in certain situations. It is generally used when the results of other tests are inconclusive. The following are typical scenarios where biopsy is advised:
- Abnormal results in blood or urine tests,
- Imaging tests showing unexpected changes in the kidneys,
- Unexpected decrease in kidney function.
How Long Does a Kidney Biopsy Take?
The duration of a kidney biopsy varies depending on several factors. Usually, the process can be completed in about 15 minutes. The duration may increase depending on the amount and detail of tissue to be examined. If comprehensive examinations will be performed on the tissue, this period may be longer. After the procedure, the following are performed to ensure the patient’s health is stable:
- Pulse control,
- Blood pressure monitoring,
These checks typically last 5–6 hours. Once the patient’s condition remains stable during this time, discharge is considered appropriate. Examination methods include light microscopy and immunofluorescence. The use of these techniques may affect the procedure time. An experienced doctor can manage the biopsy process more quickly and efficiently.
Are There Any Risks of Kidney Biopsy?
There are certain risks during kidney biopsy. Bleeding is the most common complication. After the tissue sample is taken from the patient’s kidney, mild bleeding may occur in the urine, causing a color change. Rarely, severe bleeding can occur and may require blood transfusion. In extremely rare cases, removal of the kidney may be necessary in the event of excessive bleeding.
Precautions taken before the biopsy are also important:
- Blood-thinning medications must be discontinued about five days in advance.
- The patient’s current medications and any allergies should be reported to the doctor to assess bleeding risk.
Additional risks include:
- Arteriovenous shunt formation, creating abnormal connections in kidney vessels.
- Itching on the skin after local anesthesia.
- If there is a urinary tract infection, the biopsy procedure may need to be repeated.
What Are the Advantages of Kidney Biopsy?
The advantages of kidney biopsy increase the effectiveness and reliability of this method. It plays a significant role in the diagnosis of kidney diseases. The method provides the necessary tissue samples for the accurate identification of disease. Performed with guidance from imaging techniques such as ultrasound, this procedure allows doctors to work more precisely. In addition, the biopsy is usually brief and prioritizes patient comfort.
- Minimizing pain: Anesthetic and pain relief medications are used during the procedure.
- Rapid recovery: Patients can usually return to normal life shortly after the procedure.
- Low risk of complications: The use of a thin needle reduces risks such as bleeding.
Biopsy prevents unnecessary surgical interventions, ensuring procedures are only performed when necessary. This minimizes additional burden and risks for the patient. In cases of benign diagnoses, large and invasive operations are not required.
Kidney Biopsy Reviews
For reviews of Prof. Dr. Özgür Kılıçkesmez, you can visit Google Maps or Doktortakvimi.
Frequently Asked Questions

How long does it take to recover from a kidney biopsy?
The recovery period after a kidney biopsy is generally fast. Most patients can return to daily activities the day after the procedure. However, the time required for complete recovery may vary from person to person. In general, a few days are estimated for full recovery. Especially during the first few days, it is beneficial to avoid heavy physical activities. Other factors affecting the recovery period include the patient’s overall health and any complications encountered during the procedure. Therefore, it is important for patients to follow their doctor’s recommendations and to immediately consult a healthcare facility if any abnormalities are noticed.
Is a kidney biopsy painful?
Patients generally do not feel pain during a kidney biopsy. Local anesthesia administered before the procedure completely numbs the area. In addition, sedative medications increase patient comfort. Thus, all necessary precautions are taken for pain control during kidney biopsy. As a result, patients have a comfortable experience throughout the procedure. Under these conditions, there is no pain during kidney biopsy.
What diseases are examined with kidney biopsy?
Kidney biopsy is important in diagnosing systemic inflammatory rheumatic diseases. It is especially used in the diagnosis of diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus and various types of systemic vasculitis. During this procedure, doctors take samples to determine the type and degree of inflammation in the kidney. Therefore, kidney biopsy plays a critical role in understanding the areas and severity of disease involvement. Additionally, the size and nature of the damage observed in kidney tissue are evaluated. If a mass biopsy was performed, the type of mass and whether it is cancerous is determined.
Who undergoes kidney biopsy?
Kidney biopsy is performed on patients who have blood or protein in their urine. It is also performed on those with unexplained disorders of kidney function that cannot be clarified by other diagnostic methods. This procedure is also preferred to evaluate the condition of the transplanted kidney in transplant patients. Therefore, this process is recommended for individuals determined by specific health conditions. Kidney biopsy is an important method, especially when a detailed examination of abnormalities in the kidneys is required.
Additional Resources and Documents
https://ozgurkilickesmez.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/Approach-to-Kidney-Biopsy.pdf
https://ozgurkilickesmez.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/kidney-biopsy.pdf

Interventional Radiology and Neuroradiology Speaclist Prof. Dr. Özgür Kılıçkesmez graduated from Cerrahpaşa Medical Faculty in 1997. He completed his specialization at Istanbul Education and Research Hospital. He received training in interventional radiology and oncology in London. He founded the interventional radiology department at Istanbul Çam and Sakura City Hospital and became a professor in 2020. He holds many international awards and certificates, has over 150 scientific publications, and has been cited more than 1500 times. He is currently working at Medicana Ataköy Hospital.



Vaka Örnekleri