A liver biopsy is a diagnostic procedure used to obtain a small sample of liver tissue for microscopic examination. It helps detect liver diseases, assess severity, and guide treatment strategies.
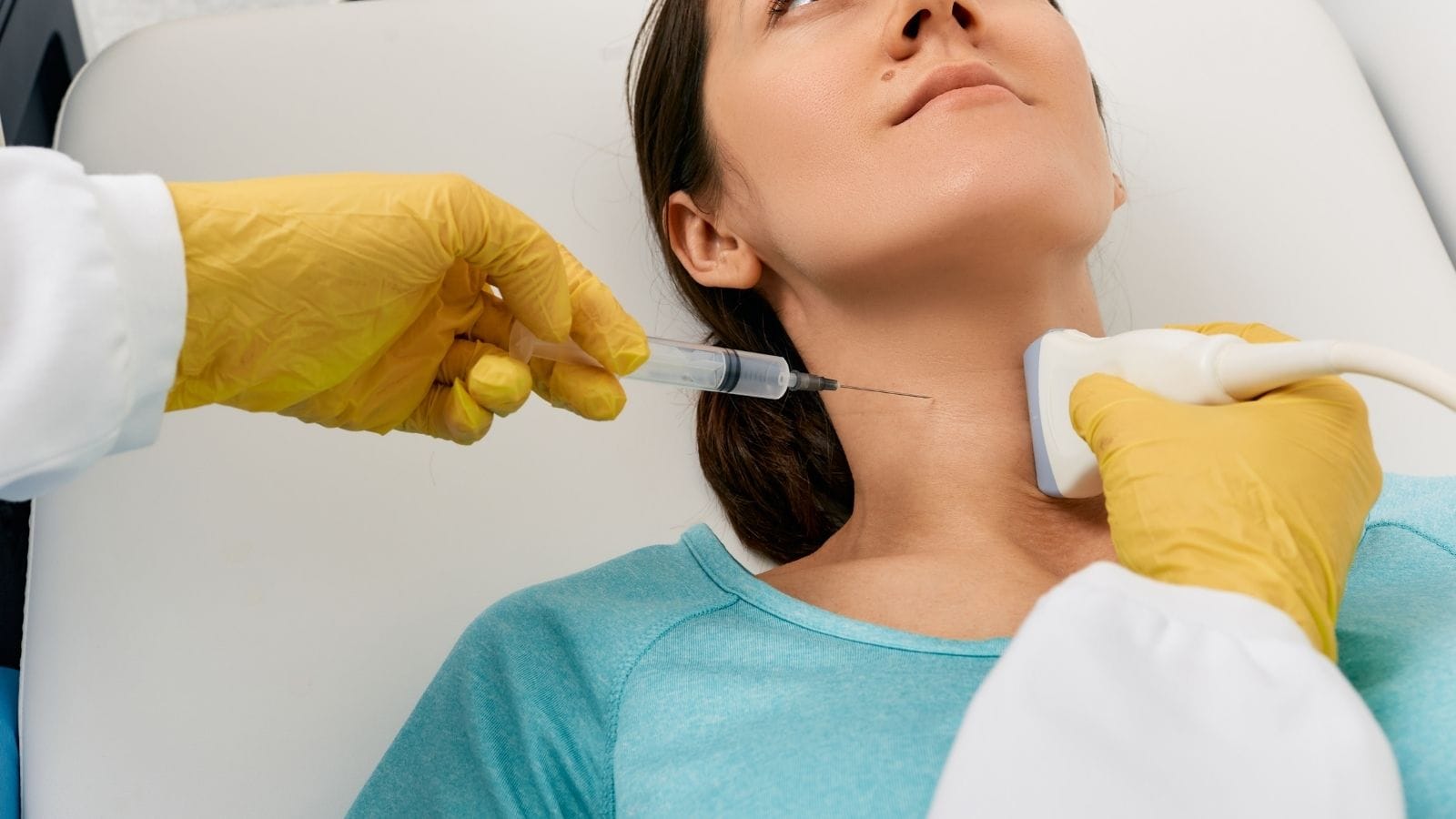
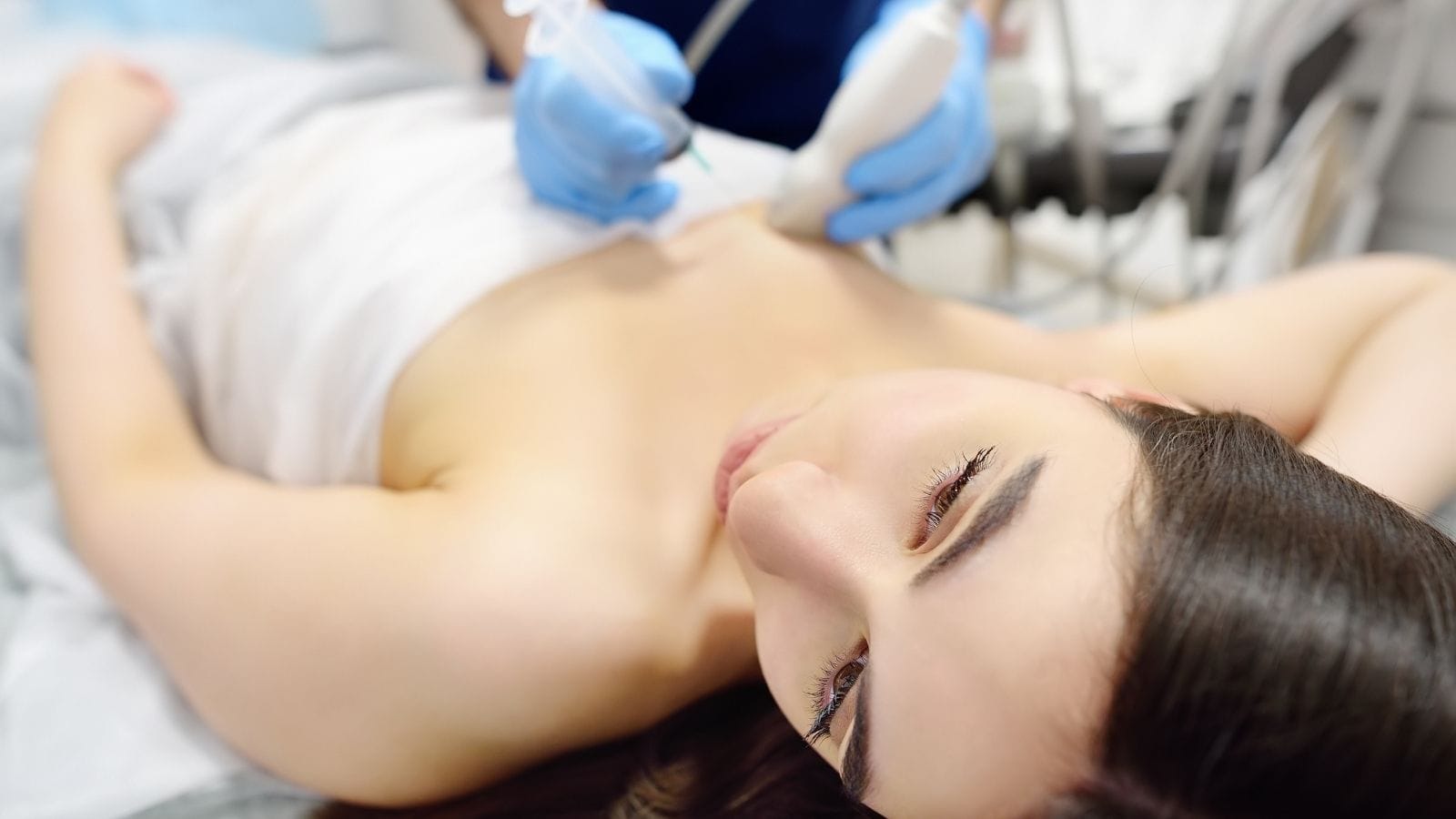
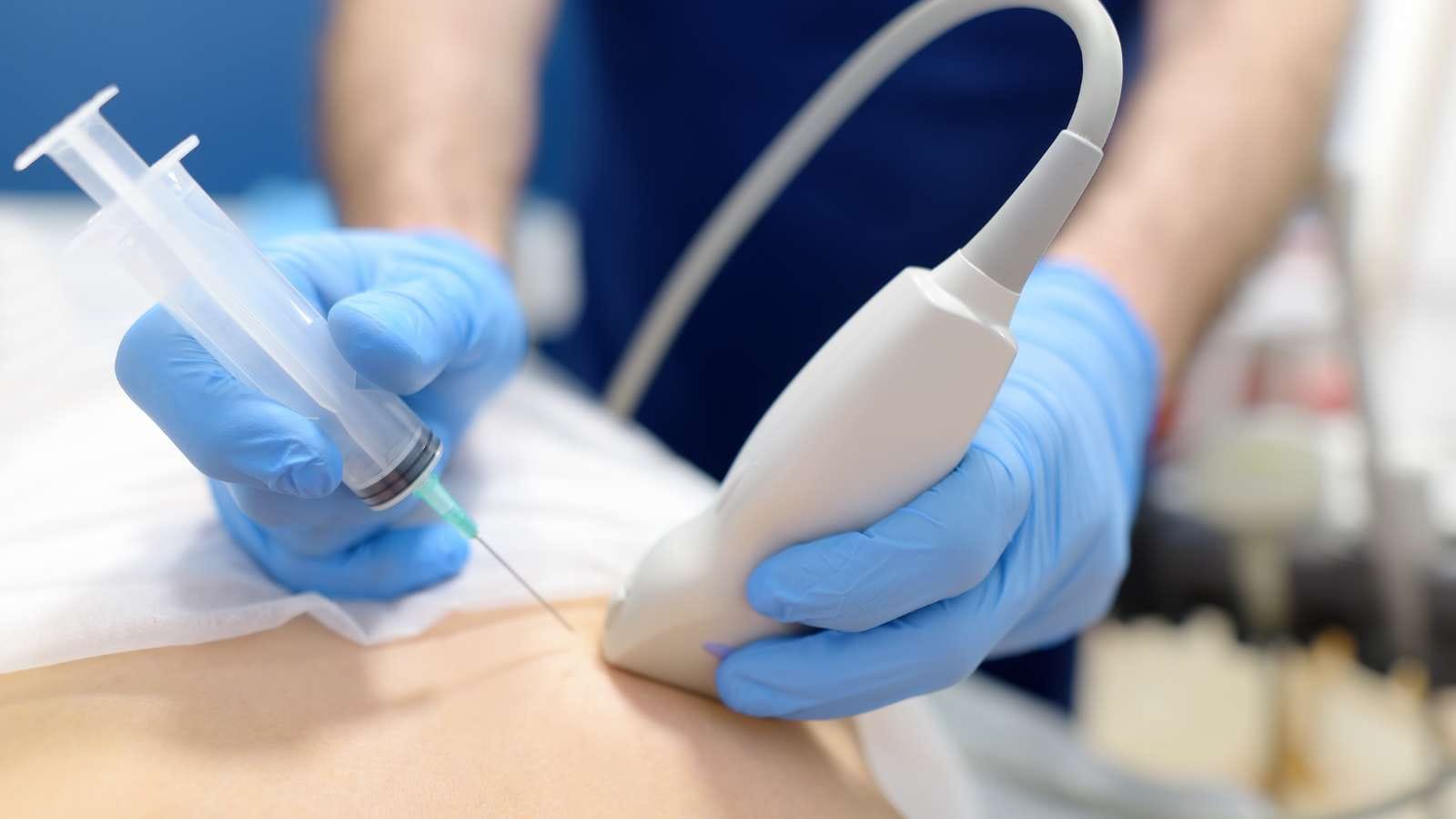
The procedure is performed with a fine or core needle under imaging guidance to ensure safety and precision. Patients may receive local anesthesia, and sedation can be used when necessary.
Liver biopsy carries a small risk of complications such as bleeding or pain, but these are generally rare. Patients are usually observed for a short period before being discharged.
This diagnostic tool is essential for evaluating chronic hepatitis, fatty liver disease, cirrhosis, and unexplained liver abnormalities. It remains the gold standard for accurate liver disease assessment.
What is a liver biopsy?
This procedure is the process of removing a small piece of tissue from the liver. Primarily, physicians may resort to this method to identify a problem related to the liver. The pathologist examines the collected tissue samples under a microscope. Through this examination, important information can be obtained about:
- The presence of disease,
- The type of disease,
- The degree of damage,
The information obtained forms the basis for guiding the treatment process. In addition, liver biopsy is not only used for diagnosis of diseases but also to assess the response to ongoing treatment. If liver function tests or imaging results show abnormal findings, doctors may recommend a biopsy.
Why is a liver biopsy performed?
Liver biopsy allows doctors to diagnose and stage liver diseases. Diseases that cannot be detected by imaging techniques can be revealed with this method. Moreover, the effectiveness of ongoing treatment can also be assessed with this procedure. For patients who have undergone a liver transplant, biopsy is an important tool for monitoring the function of the new organ. Especially in cases without significant symptoms, liver biopsy can be vital. The procedure is frequently performed for the following reasons:
- Liver problems that cannot be determined by blood tests and imaging methods,
- Staging of liver diseases,
- For treatment planning and evaluating the effectiveness of ongoing treatment,
- Monitoring the condition of the organ after liver transplantation,
- Detection of masses or abnormalities in the liver,
- Recurrent and unexplained fever.
These situations constitute the main reasons for performing liver biopsy. Serious health problems such as chronic hepatitis, autoimmune diseases, and genetic disorders can be more clearly understood with this procedure.
When is a liver biopsy performed?
Liver biopsy is a medical procedure performed under various conditions. Especially when suspicious masses are detected in the liver, it is recommended to plan this procedure. To reach the targeted mass, the procedure is performed under the guidance of ultrasound or computed tomography by an interventional radiologist. In cases such as advanced obesity, the blind biopsy method may not be feasible, so alternative methods should be considered. The timing of liver biopsy:
- In the presence of suspicious liver masses,
- When a clear diagnosis cannot be made with imaging methods,
- When alternative methods need to be considered for patients with advanced obesity.
What should be asked to the physician before and after a liver biopsy?
Information that patients should share with their physicians before and after a liver biopsy is very important. In particular, detailed information should be provided about allergies and other existing illnesses. If medications are being used, these should be reported to the doctor. The types of medications that should be reported to the doctor are listed below:
- Anticoagulants (blood thinners)
- Diabetes medications
- Anti-inflammatory drugs
- Dietary supplements
In addition, drugs that affect coagulation or those that interact with sedatives may be temporarily discontinued before the procedure.
How is a liver biopsy performed?
During a liver biopsy, the patient is usually placed in a supine position. First, the biopsy area is carefully cleaned with an antiseptic solution. After cleaning, local anesthesia is applied to numb the skin where the needle will enter. Then, a small incision is made in the skin to allow easy access of the needle to the liver. The path of the needle is monitored by radiological methods to increase the safety of the procedure. The needle is advanced through the ribs into the liver, and the necessary tissue samples are collected.
What are the risks associated with liver biopsy?
Liver biopsy is generally safe when performed by an experienced physician. However, certain risks may occur in some cases:
- Pain in the rib area and right shoulder is a common occurrence after biopsy.
- Bleeding is another problem that may arise after liver biopsy, though it is rare.
- Infection is a rarely encountered but possible risk.
- In very rare cases, the gallbladder or surrounding tissues may be damaged. These risks are minimized by ultrasound examination before the procedure.
In patients who undergo transjugular biopsy:
- Hematoma may occur at the site where the catheter is placed.
- Additionally, this procedure may sometimes affect the nerves, which can lead to temporary neurological effects such as drooping eyelid.
What happens after a liver biopsy?
There are certain steps to be followed after a liver biopsy. After the procedure, pain may be felt at the biopsy site and sometimes in the shoulder. This pain can be alleviated with simple painkillers. Cold compresses are recommended for the patient and rest is advised. The patient is also kept under constant observation:
- Blood pressure and pulse are regularly monitored.
- Ultrasound is performed when necessary to assess the risk of bleeding.
- Blood tests are performed at regular intervals until the patient is discharged.
If the biopsy was performed under sedation, the patient should not be left alone for 12 hours. During this period, the patient should avoid:
- Driving,
- Daily activities such as cooking.
It is especially important to rest and avoid heavy lifting for the first two days after the procedure.
What are the advantages of liver biopsy?
- Allows accurate diagnosis of disease.
- Guides the treatment process.
- Clarifies the severity and spread of the disease.
- Enables assessment of the patient’s response to treatment.
What are the types of liver biopsy?
Liver biopsy is a fundamental method in the diagnosis and management of diseases and is performed with three different techniques. Each method is preferred based on specific situations and the patient’s health status.
**Percutaneous biopsy** is the most commonly used method for obtaining tissue samples from the liver. In this technique, the liver is accessed directly through the skin with a needle. Ultrasound or CT is used during the procedure to ensure that the sample is taken from the correct area.
**Transjugular biopsy** is especially suitable for patients with fluid accumulation in the abdomen. In this method, a needle is inserted into the jugular vein in the neck and reaches the liver through the veins. This way, the risk of bleeding in a liver floating in fluid in the abdomen is reduced.
**Surgical biopsy** is usually performed during another surgical procedure. If the patient is already undergoing surgery, a liver sample can be taken at that time.
Is the patient sedated during biopsy?
Whether sedation is applied during liver biopsy depends on the type of procedure. Generally, during standard blind biopsy, the patient remains conscious and only local anesthesia is used. The patient may be required to control their breathing, for example, by being asked to hold their breath or breathe in and out on command.
**Targeted Biopsy:**
- Usually performed under ultrasound or CT guidance.
- A needle is directed toward a specific lesion.
- Sedation is more common in this type of biopsy.
Frequently Asked Questions

How long does a liver biopsy take? A liver biopsy usually takes about 15 minutes. First, local anesthesia is administered, and then the actual biopsy procedure begins. With the help of a small incision made in the skin, the biopsy is completed within 3–4 minutes. Therefore, including preparation and completion times, the patient should set aside about 15 minutes for the procedure.
Is a liver biopsy painful? Due to the mild sedation applied during liver biopsy, pain is generally not felt. However, after the procedure, some people may report mild pain in the area where the procedure was performed and in the right shoulder. These pains are usually treated with simple painkillers and go away within a few days. Therefore, with managed sedation and simple precautions, liver biopsy is generally considered a painless procedure.
What should be considered after a liver biopsy? After liver biopsy, the patient can start consuming fluids two hours after the procedure. After four hours, they can continue eating various foods. On the other hand, it is important for the patient to avoid strenuous physical activity for twenty-four hours. During this time, activities that may put stress on the body should be avoided. These precautions help reduce the risk of complications after the procedure and support rapid recovery.
Can food be eaten after a liver biopsy? After liver biopsy, the patient can start with fluid intake during the first two hours. During this period, simple beverages such as water can be consumed. After the first two hours, the patient can gradually return to a normal diet. Especially after four hours, it is recommended to return to a normal eating routine, including solid foods, as much as their health allows. Therefore, eating can be resumed after four hours, and as long as the patient feels comfortable, it is generally safe to continue regular meals.
In what position is a liver biopsy performed? Liver biopsy is usually performed in the supine position. The patient is made to lie comfortably, and an appropriate environment is prepared for the procedure. This position makes it easier for the doctor to access the liver and to obtain tissue samples from the correct spot under ultrasound guidance. It also helps increase patient safety during the procedure. Therefore, lying supine during a liver biopsy is considered the most appropriate position for both the doctor and the patient.
How long does it take to get liver pathology results? The time to obtain liver pathology results varies depending on the characteristics of the tissue examined and the complexity of the suspected disease. In general, it takes between two and ten days to receive liver pathology results, depending on whether additional tests are required. Therefore, patients and doctors have to wait for results during this time frame to determine a definitive diagnosis. The results obtained during this process play a critical role in directing the patient’s treatment.
Additional Resources and Documents

Interventional Radiology and Neuroradiology Speaclist Prof. Dr. Özgür Kılıçkesmez graduated from Cerrahpaşa Medical Faculty in 1997. He completed his specialization at Istanbul Education and Research Hospital. He received training in interventional radiology and oncology in London. He founded the interventional radiology department at Istanbul Çam and Sakura City Hospital and became a professor in 2020. He holds many international awards and certificates, has over 150 scientific publications, and has been cited more than 1500 times. He is currently working at Medicana Ataköy Hospital.



Vaka Örnekleri