Interventional radiology is a medical specialty that uses imaging guidance to perform minimally invasive treatments. Instead of open surgery, catheters, wires, and needles are used to access diseased areas, providing effective therapy with fewer risks and shorter recovery.
Vascular diseases are frequently treated with interventional radiology. Techniques such as angioplasty, stenting, and embolization restore blood flow, treat aneurysms, or stop internal bleeding. These methods reduce surgical complications while offering precise and durable solutions.
Oncological applications of interventional radiology include tumor ablation and embolization. Using radiofrequency, microwave, or chemoembolization, targeted cancer treatments are performed directly on tumors, minimizing systemic side effects and preserving surrounding healthy tissue.
Pain management and drainage procedures are also part of interventional radiology. Image-guided injections, abscess drainage, and fluid aspiration provide rapid relief and accurate diagnosis. This wide range of procedures shows the versatility and importance of interventional radiology in modern medicine.
[https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WKlzgOLqBGk](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WKlzgOLqBGk)
Arterial Occlusions
Arterial occlusions can cause serious health problems. This condition occurs due to clot formation, atherosclerosis, and other reasons. Interventional radiology techniques are used in the diagnosis and treatment of these occlusions. Angiography allows visualization of the problematic area by injecting a high-density substance into the vessel. The identified occlusions or narrowings can be treated with minimally invasive interventions. The main approaches used include balloon, drug-coated balloon, stent, atherectomy, and clot removal. These methods:
- Offer a less painful and faster recovery process for the patient.
- Carry a lower risk of complications.
- Usually do not require hospitalization.
Endovascular Treatment of Aneurysm (Vascular Ballooning)
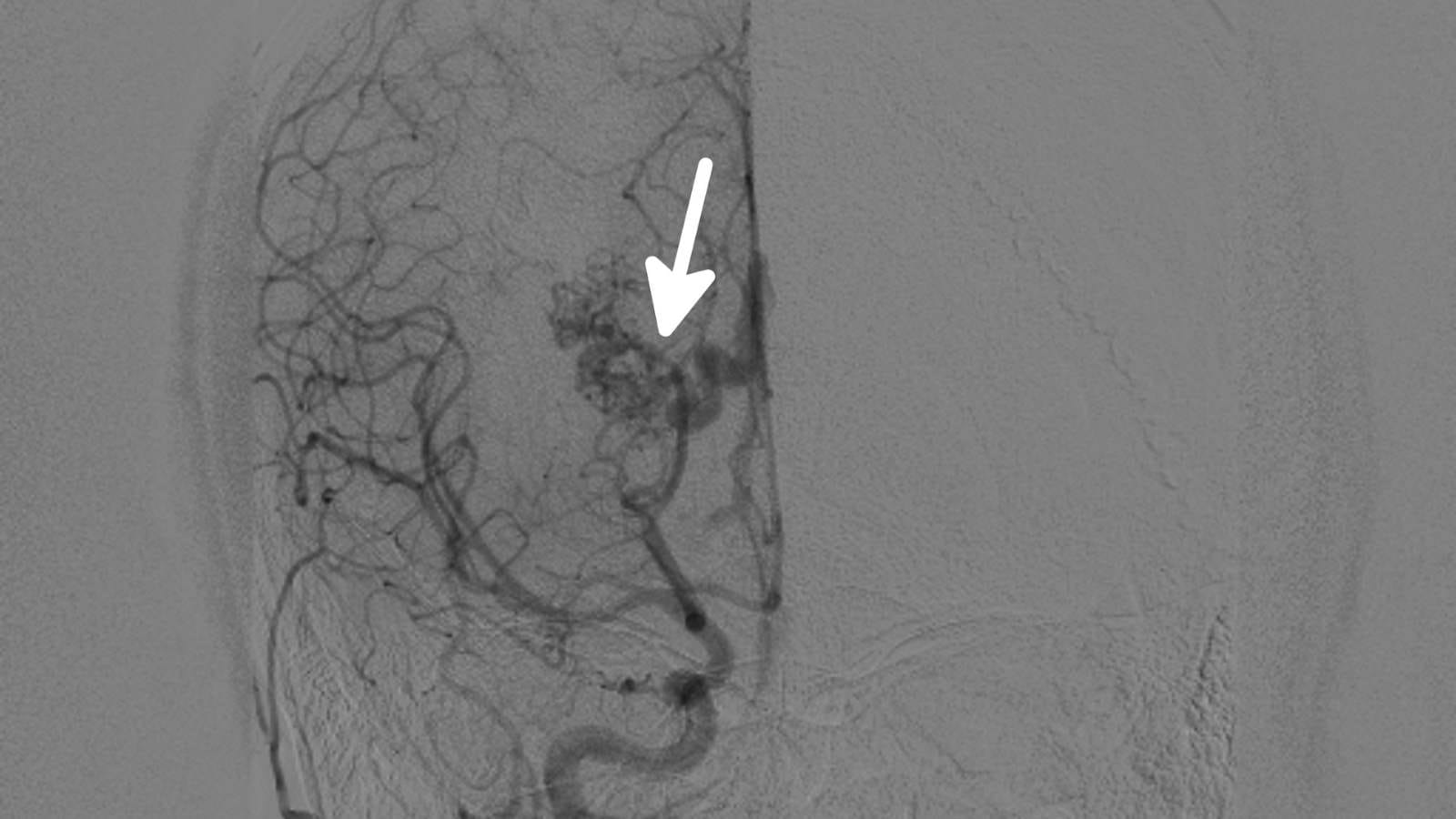
Aneurysms are formed by balloon-like enlargement of weak spots in vessel walls. These structures can rupture under blood pressure and cause severe bleeding. Especially in the brain and other internal organs, this can lead to life-threatening complications. At this point, interventional radiology comes into play:
- The location and size of the aneurysm are determined by angiography.
- If deemed appropriate, coil, stent, or stent-assisted coil placement is performed.
- The stent restricts blood flow in the area where the aneurysm is located.
This method greatly reduces the risk of rupture and offers a safe treatment alternative for the patient. The treatment process is tailored to the patient’s condition and allows for control of the aneurysm. Thus, patients can experience a faster and more effective recovery with a less invasive method. In interventional radiology, this is one of the rare treatments performed under general anesthesia, as even a millimetric movement can cause complications, so the patient must be completely still under deep anesthesia. Essentially, this is not because the procedure is painful.
Leg Artery Occlusions
These occlusions, more common in older age groups, present with symptoms such as pain in the calf, numbness, coldness, paleness, and sometimes bruising in the toes. As the condition progresses, poor circulation can lead to ulcers and more serious problems such as gangrene. Interventional radiology techniques successfully address these vascular issues:
- Angiography
- Balloon therapy
- Stent placement
- Atherectomy
- Clot removal
These techniques open blockages in the vessels, normalize blood flow, and help overcome related health problems.
Carotid Artery (Neck Artery) Stenosis
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-b_JWOMYCZA
The carotid artery, one of the main arteries in the neck, carries blood to the brain. Narrowing and blockages in this artery can cause various neurological problems. Such blockages are usually caused by atherosclerosis. These blockages in the carotid artery can reduce brain function or lead to serious conditions such as stroke. Interventional radiology techniques play an important role in the treatment of these vascular problems. During the procedure:
- The narrowed area is visualized in detail using angiography.
- A filter is placed to prevent embolism to the brain, and the vessel is opened by stent placement.
Opening Dialysis Fistula Occlusions
Occlusions in fistulas, which are vital for dialysis, can interrupt patients’ treatment processes. Interventional radiology techniques are used to resolve these occlusions:
- Thrombolysis: Used to dissolve clots.
- Thrombectomy: Preferred for mechanically removing clots.
- Balloon angioplasty: A balloon is used to widen the narrowed area.
- Stent placement: A stent is placed to prevent the reopened vessel from narrowing again.
These methods open occlusions in fistulas, allowing dialysis patients to continue their treatment uninterrupted and without delay.
Buerger’s Disease
Buerger’s disease is a peripheral vascular disease commonly seen in male smokers. This condition affects the small and medium-sized vessels in the arms and legs. Treatment of the disease is supported by interventional radiology methods such as angioplasty. It is known that exposure to tobacco products plays a critical role in the development of the disease. Immune system disorders and genetic predispositions are also effective in the onset of the disease.
- The mechanism of the disease is unknown; however, factors such as immunological dysfunction and hypersensitivity to tobacco are predominant.
- If smoking is not stopped, vessels opened during the procedure will quickly close again.
A large proportion of patients who continue to smoke may face serious health problems over time. Among these, the need for amputation is significant. Although the disease rarely causes death, it is a condition that seriously reduces quality of life.
Myoma Treatment (Myoma Embolization)

During this procedure, the uterine vessels are targeted. By embolizing the vessels feeding the fibroids, the fibroids shrink. This procedure can significantly reduce pain, discomfort, and excessive bleeding experienced by patients. The method offers the following advantages:
- Reduction of pain and discomfort,
- Elimination of difficulties during urination,
- Regulation of menstrual irregularities.
All fibroids can be neutralized at the same time in a single procedure. Therefore, if the patient does not want a hysterectomy (removal of the uterus) for certain reasons, this is the most effective method. After the procedure, there is significant abdominal pain lasting about a day, so patients are hospitalized for one day.
Varicocele Treatment
Varicocele is a health problem directly associated with infertility in men. It occurs as a result of abnormal enlargement of the veins in the testicles. This increases the temperature in the testicles and leads to loss of function of sperm cells. Interventional radiology techniques offer solutions for varicocele treatment:
- Access is achieved through minimally invasive interventions in the groin region.
- Endovascular treatment methods are used.
- Special agents are injected into the vessels to block the varicose veins.
- Its advantage over surgery is that the procedure takes about 30 minutes and discharge can be done 1-2 hours later. Also, since we can access the dilated vessels from the opposite side, side branches that cannot be seen in surgery can be closed, so recurrence of the disease is extremely rare.
Procedures Supporting Oncological Treatment
Biopsy of cancerous tissue plays an important role in the cancer treatment process by identifying the cancer and determining the tumor subtype. Supported by imaging techniques, this method enables tumor samples to be taken without the need for surgery. This procedure is usually completed in as little as 15 minutes. Fast and minimally invasive biopsy allows patients to have an easier treatment process. In addition:
- The healing process is accelerated.
- The need for challenging surgical interventions is reduced.
- Positive effects are observed on patients’ overall health.
Direct Cancer Treatment Procedures
Interventional radiology offers various techniques used especially for cancer treatment in the field of oncology. These modern medical methods target cancerous tissues and provide treatment options. Some of the most commonly used methods are as follows:
- Radiofrequency ablation
- Microwave ablation
- Irreversible Electroporation (IRE)
- Chemoembolization (TACE)
- Intra-arterial chemotherapy
- Radioembolization (TARE)
- Chemosaturation
These techniques directly target diseased tissues while minimizing the risk of damaging healthy tissues. Patients can experience a faster and less painful recovery with these minimally invasive procedures. These methods are repeatable, allow for combination treatments, and increase effectiveness. All are non-surgical and performed while the patient is awake.
Needle Biopsies
Needle biopsies are an important application of interventional radiology. With this method, doctors can take samples from various organs in the body. Ultrasound or computed tomography is used during the procedure. Thus, the target organ can be reached accurately and safely. Needle biopsy is performed without the need for major surgery. Therefore, the recovery period is shorter and the risk of infection is reduced. Organs from which samples can be taken by needle biopsy include:
- Liver
- Breast
- Lymph nodes
- Prostate
Basic Drainage Procedures (Biliary and Urinary Tracts)
Drainage procedures applied especially in obstructions of the bile ducts and urinary tract are a significant area of application. This treatment method is performed with a minimally invasive approach. These procedures, performed under local anesthesia, offer less pain and a faster recovery process for patients. During the procedure:
- Obstructions in the bile ducts,
- Obstructions in the urinary tract,
are successfully resolved. After drainage, fluid accumulations are removed and acute problems are quickly resolved. The focus then shifts to treating the underlying disease. In this way, patients can return to their normal lives more quickly.
Cyst-Abscess Treatments
With the help of radiological imaging techniques, especially using a needle, fluid accumulations in the body are drained. This treatment method is performed under local anesthesia and usually results in the patient being discharged on the same day. During drainage, fluid-filled structures such as abscesses or cysts are successfully drained and there is no incision in the body.
The advantages of these treatments are as follows:
- Anesthesia is generally not required.
- The procedure is performed through an opening as small as a needle puncture.
- Patients usually go home the same day as the procedure.
- The procedures are simple and carry less risk.
- The return to normal life is faster.
As a result, interventional radiology offers a minimally invasive solution in the treatment of problems such as cysts and abscesses.

Interventional Radiology and Neuroradiology Speaclist Prof. Dr. Özgür Kılıçkesmez graduated from Cerrahpaşa Medical Faculty in 1997. He completed his specialization at Istanbul Education and Research Hospital. He received training in interventional radiology and oncology in London. He founded the interventional radiology department at Istanbul Çam and Sakura City Hospital and became a professor in 2020. He holds many international awards and certificates, has over 150 scientific publications, and has been cited more than 1500 times. He is currently working at Medicana Ataköy Hospital.





Vaka Örnekleri